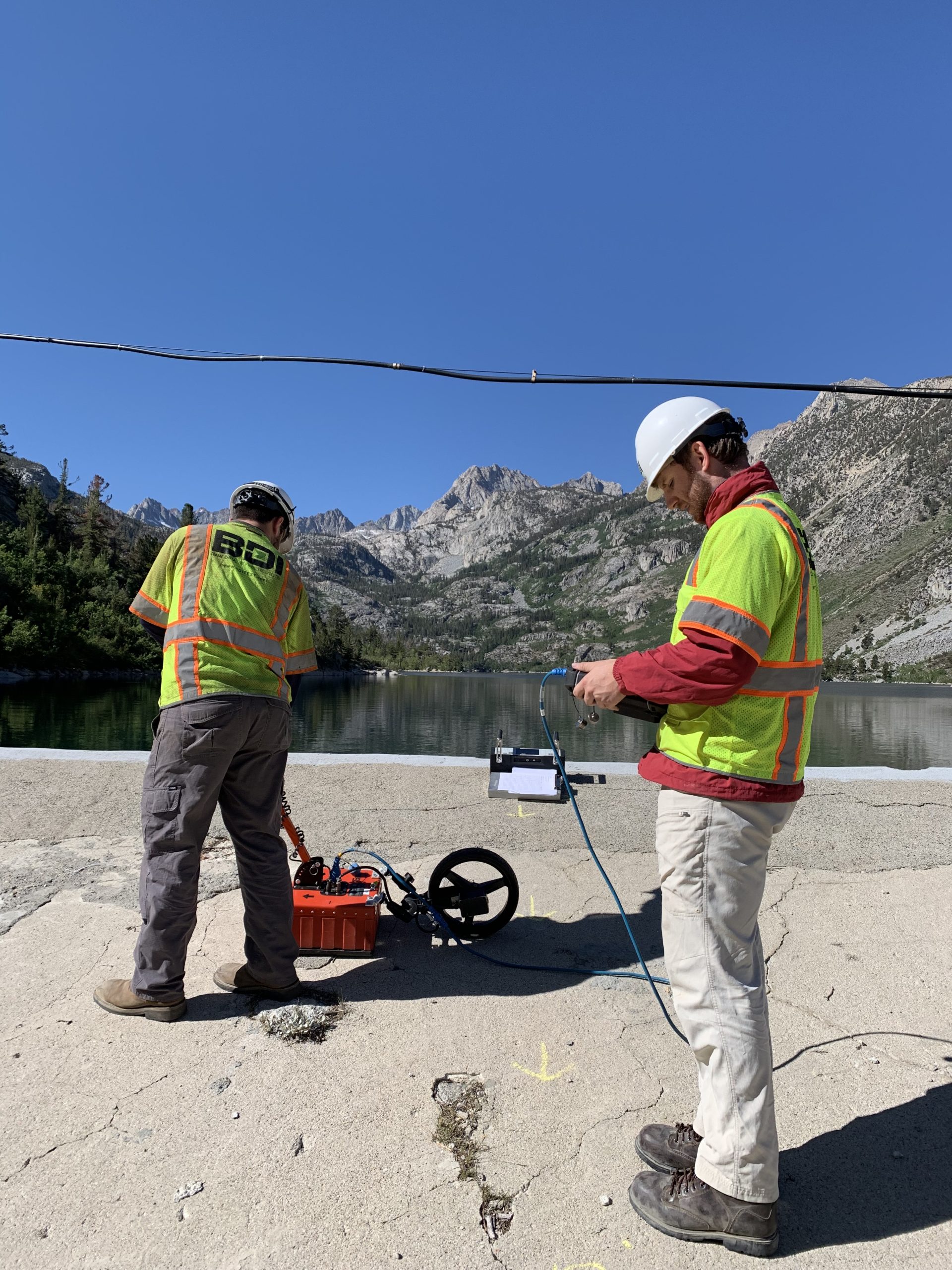
What is Nondestructive Testing & Evaluation (NDT-E)?

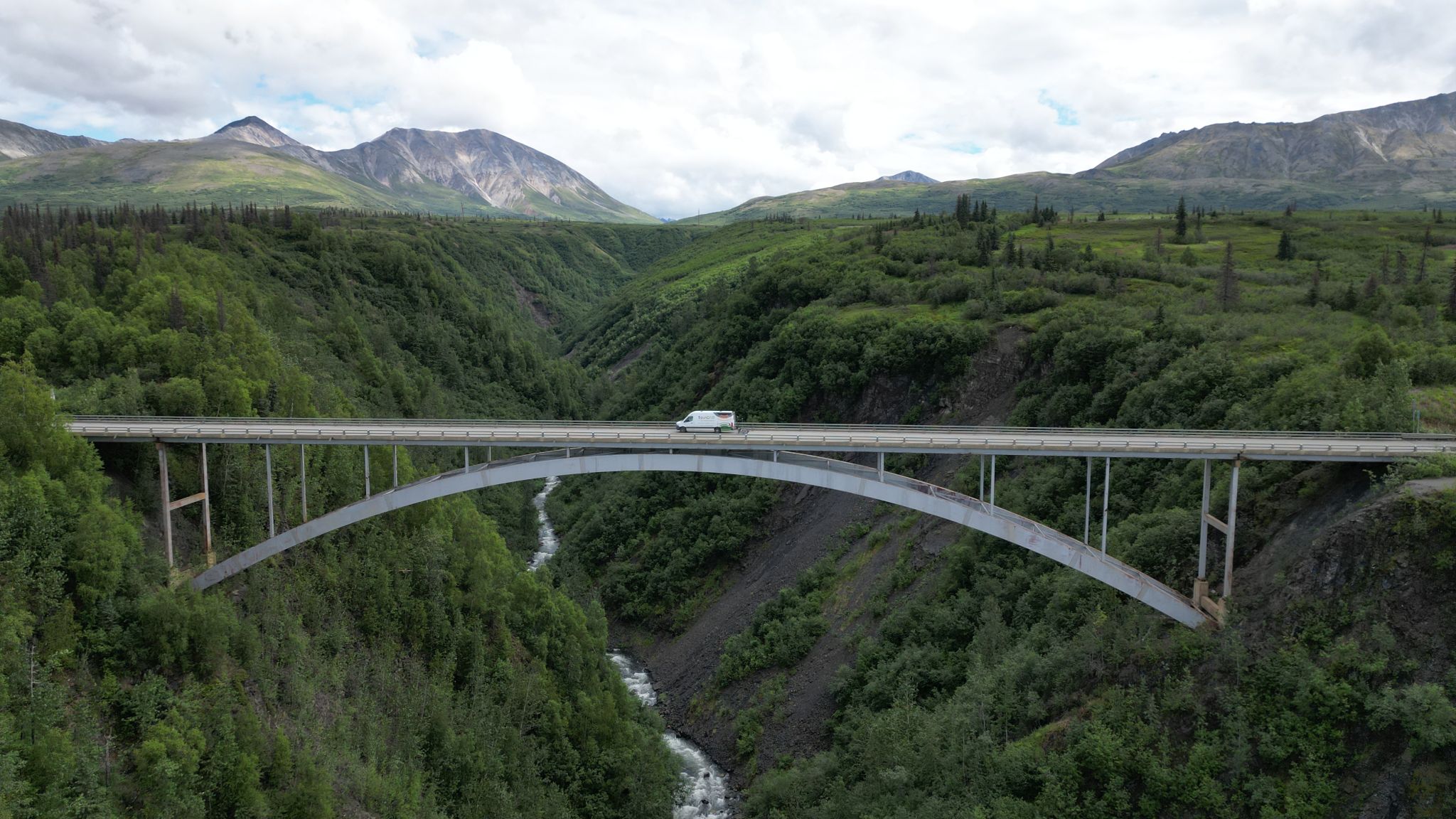
NDT-E represents a collection of tools, techniques, and technologies that are used to answer questions about the condition and configuration of different structures without damaging them or affecting their ability to function.
Whether it’s locating steel reinforcement in a concrete tunnel liner, measuring the length of an unknown foundation, or classifying corrosion and spalls along a bridge deck, NDT-E methods can provide asset owners with valuable insights to inform their engineering judgments, maintenance planning, and overall service approaches.
As a recognized industry authority on NDT-E, BDI offers both the technical expertise and field experience necessary to generating these insights on-time and on-budget as well as the professional engineering and analytical services needed to ensure results are accurate and actionable.
How We Measure
-
Concrete
-
Geophysical
-
Steel
-
Timber
 Impact Echo (IE)
Impact Echo (IE)
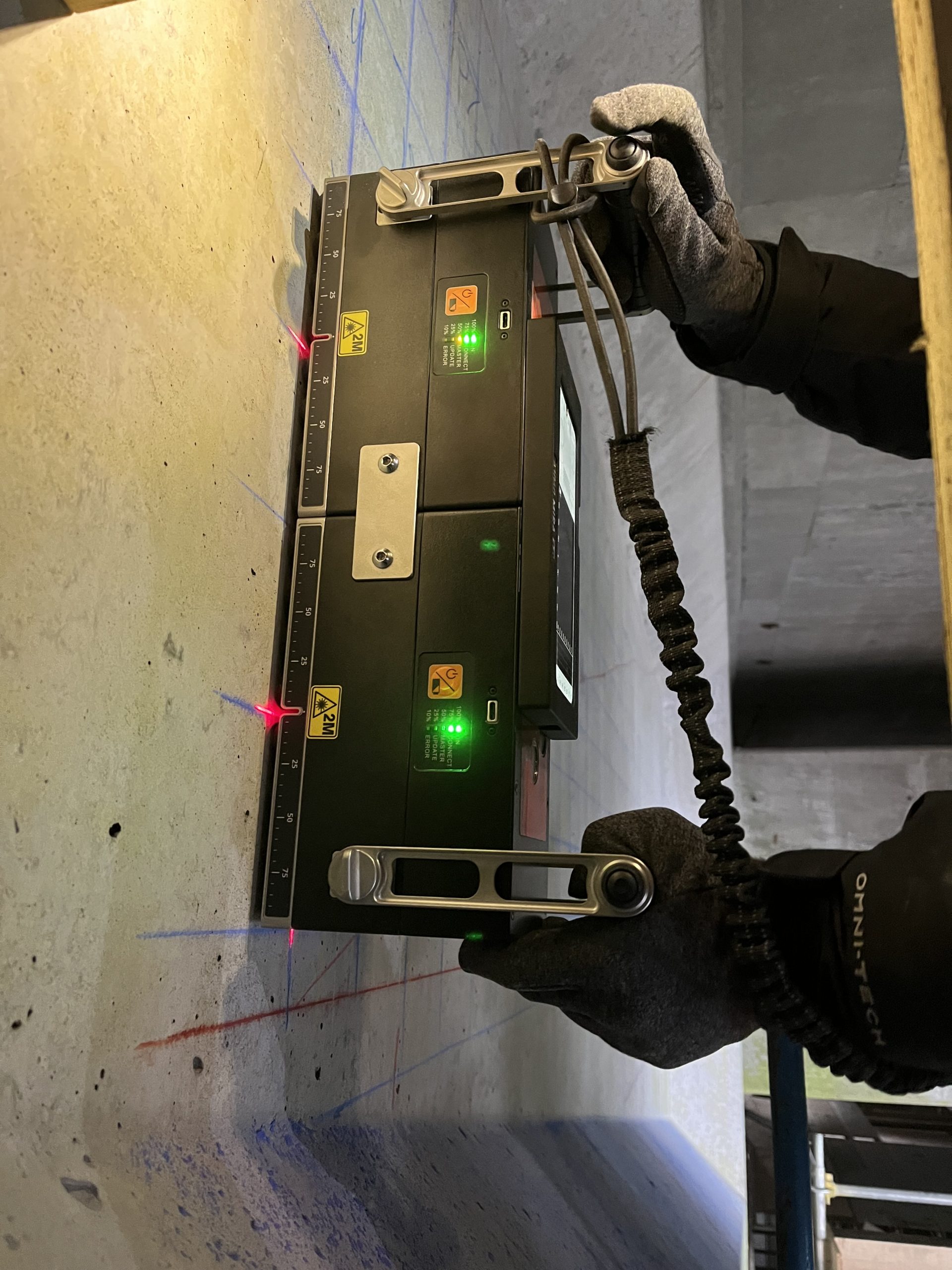
 Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR)
Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR)
 Infrared Thermography (IR)
Infrared Thermography (IR)
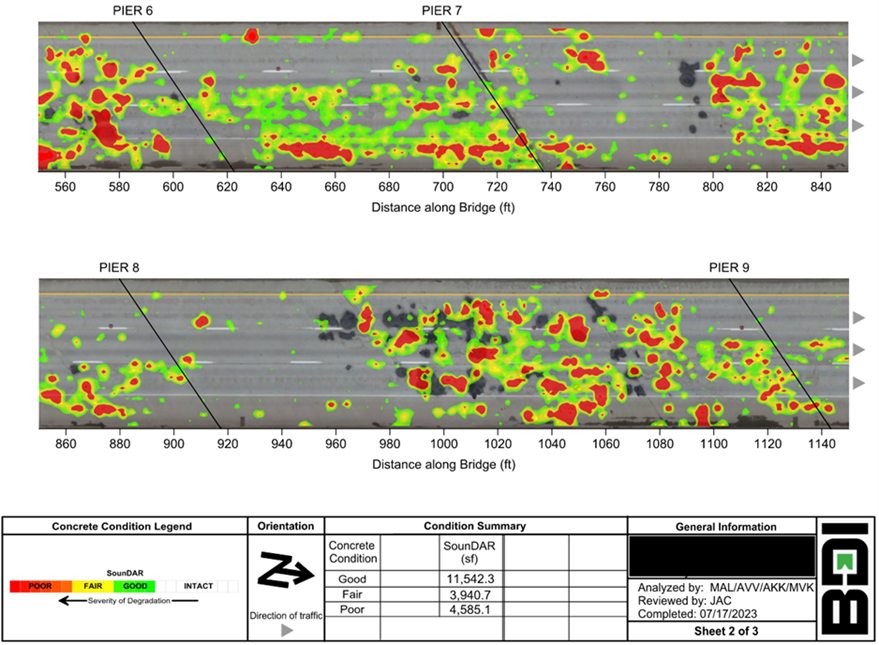
 Deck Acoustic Response (SounDAR) – automated concrete sounding
Deck Acoustic Response (SounDAR) – automated concrete sounding
 High-Resolution Imaging (HRI)
High-Resolution Imaging (HRI)
 Ultrasonic Tomography (MIRA)
Ultrasonic Tomography (MIRA)
 Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity (UPV)
Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity (UPV)
 Half Cell Potential Testing (HCP)
Half Cell Potential Testing (HCP)
 Sonic Echo-Impulse Response (SE-IR)
Sonic Echo-Impulse Response (SE-IR)
 Electrical Resistivity Testing (ER)
Electrical Resistivity Testing (ER)
 Rapid Chloride Testing (RCT)
Rapid Chloride Testing (RCT)
 Hammer Sounding & Chain Drag
Hammer Sounding & Chain Drag
 Visual Inspection
Visual Inspection













 Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR)
Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR)
 Electromagnetic Methods
Electromagnetic Methods
 Crosshole Sonic Logging (CSL)
Crosshole Sonic Logging (CSL)


 Ultrasonic Testing (UT)
Ultrasonic Testing (UT)
 Phased Array Ultrasonic Testing (PAUT)
Phased Array Ultrasonic Testing (PAUT)
 Magnetic Particle (MT)
Magnetic Particle (MT)
 Magnetic Flux Leakage (MFL)
Magnetic Flux Leakage (MFL)
 Acoustic Differential Method
Acoustic Differential Method



 Sonic Echo-Impulse Response (SE-IR)
Sonic Echo-Impulse Response (SE-IR)
 Ultraseismic Testing (US)
Ultraseismic Testing (US)
 Parallel Seismic Testing (PS)
Parallel Seismic Testing (PS)

What We Deliver
Beyond standard narrative reporting and conclusions, BDI provides:
Innovative Solutions
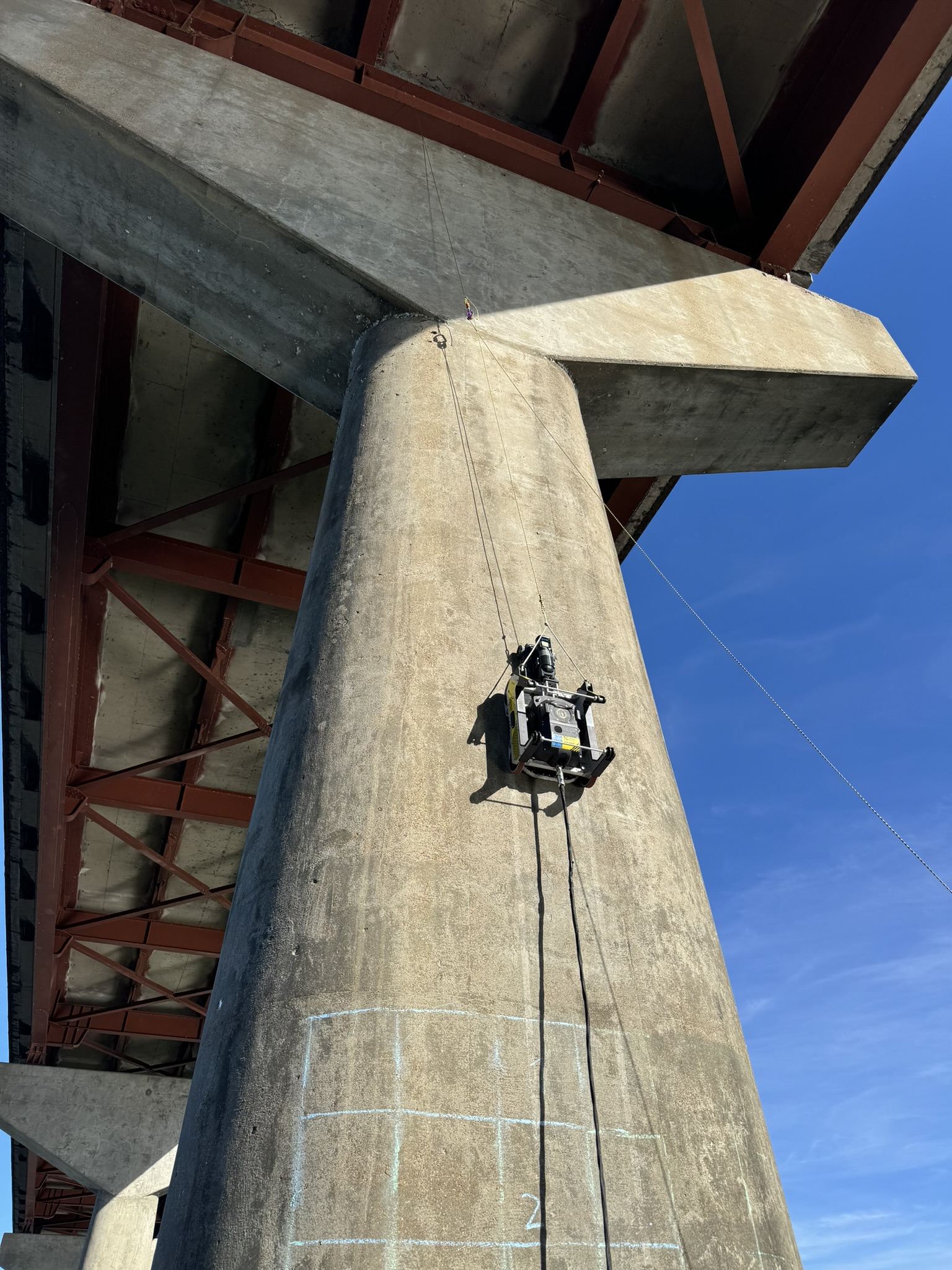
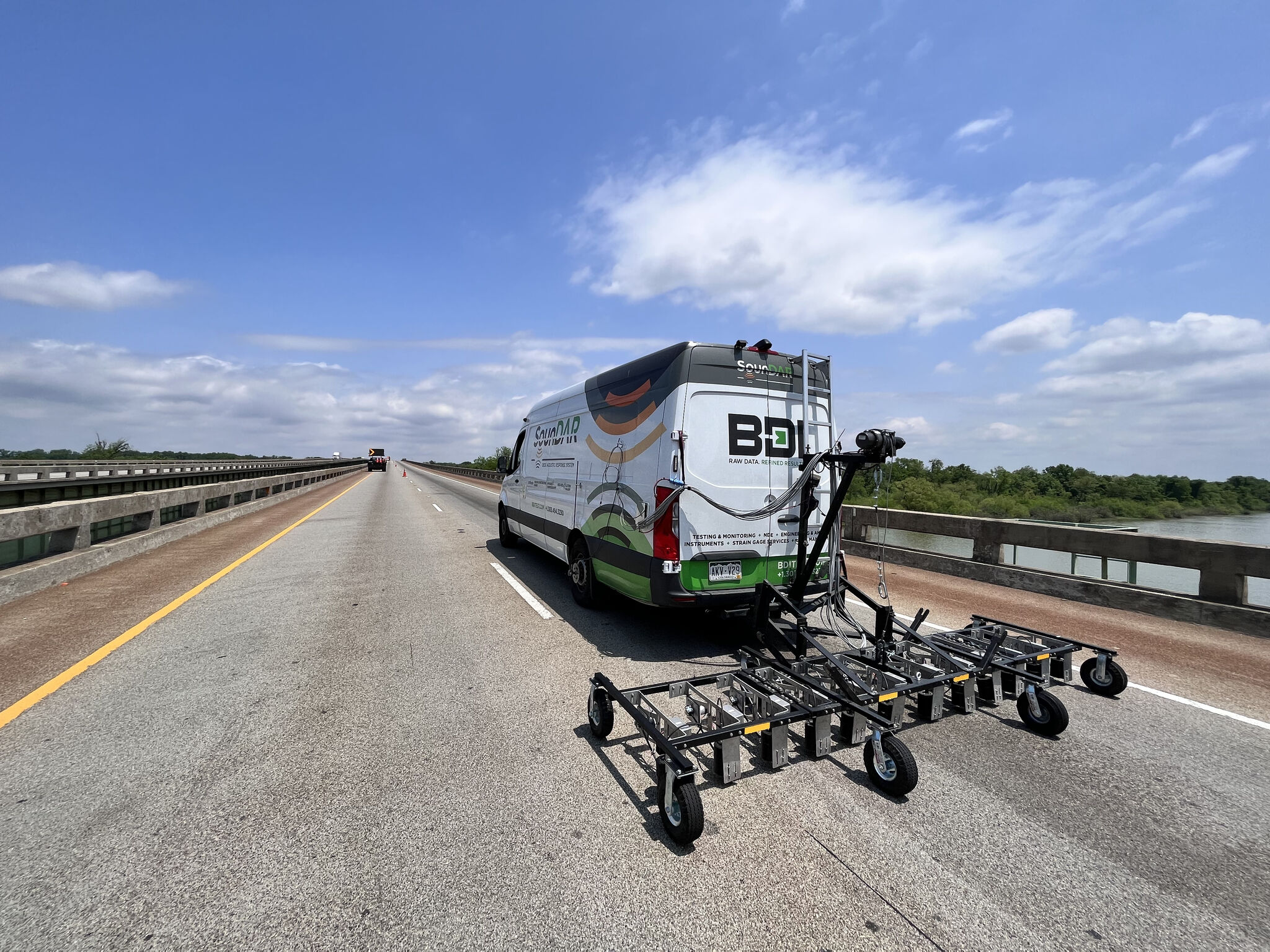
Aerial imaging, vehicle-based NDE scanning, and traditional testing methods are strategically combined to deliver quantitative information for improved asset management.
Contact Us With Any Questions
Bridge Diagnostics, Inc. ensures non-discrimination in all programs and activities in accordance with Title VI of the Civil Rights Act of 1964. If you need more information or special assistance for persons with disabilities or limited English proficiency, contact our office at +1.303.494.3230 Ext. 116


 Condition and Integrity Assessment
Condition and Integrity Assessment